Dart Mixins
Posted on April 20, 2020 in Dart

Introduction
Mixins keep Dart code reusable across separate classes. It's the most efficient way to reuse common code from multiple classes that share common behaviors.
A mixin class contains methods to be used by other classes without being their parent. This is how mixins differ from interfaces and abstract classes.
Mixins are declared using keyword mixin like below:
mixin SharedBehavior {
}
Let's understand this with help of the example of different people with different occupations: artist, engineer, doctor, and sportsman. Let's think in terms of OOP manner, representing people in their classes.
Personclass: The most common properties could be abstracted in classPersonthat other classes would extend from. Common properties (like age , name etc) and common behaviors (like eat and sleep) can go in here.
abstract class Person {
int age;
int name;
eat() {}
sleep() {}
}
-
Artistclass: Our artist is a Person. Makes landscapes sketches. -
Engineerclass: The engineer is a Person. Makes buildings sketches and reads research papers on construction. -
Doctorclass: The doctor is a Person. Reads daily on latest health news and likes to do workout. -
Boxerclass: The boxer is a type of Athlete. Athlete is a Person. Boxer does routine exercises as well practices punches.
As we see from above that artist does sketching. Engineer does sketching as well as reading. Doctor does reading and exercise. The athlete does exercise. The boxer-a type of athlete, also does boxing.
Let's see a visual representation in diagram below:
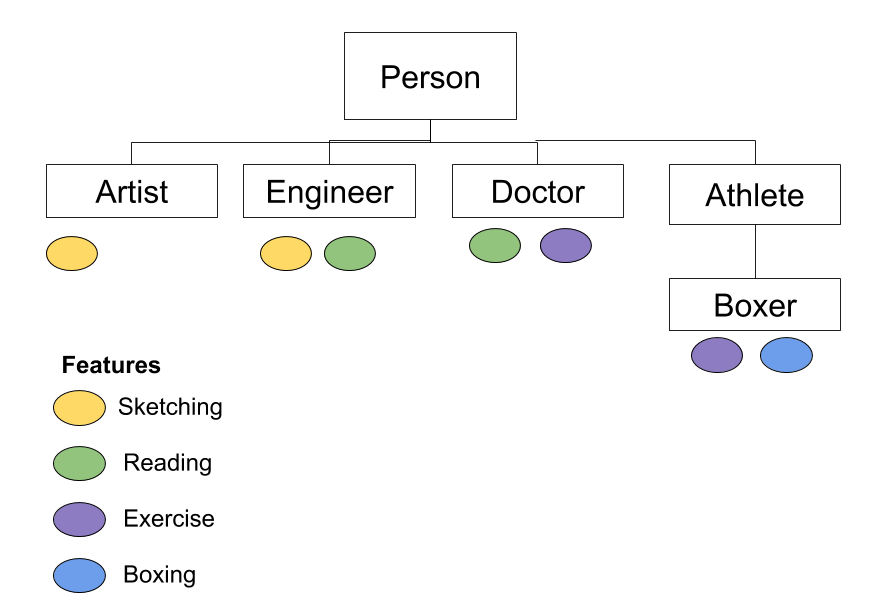
Such overlapping common behaviors can be extracted into mixins. Let's create mixins next.
Creating Mixins
Sketching
The Sketching mixin defines the common sketch() method. It takes a message and prints it on console to keep things simple for demonstration.
mixin Sketching {
sketch(String message) {
print(message);
}
}
Reading
The Reading mixin defines dailyReading(String topic) method. A reading topic is passed as parameter.
mixin Reading {
dailyReading(String topic) {
print("Daily reading on ${topic}");
}
}
Exercise
The Exercise mixin defines methods for running and weight training. The running(int mile) method passes mile parameter to print the message. The weightTraining(int weights) method prints the value for weights parameter.
mixin Exercise {
running(int mile) {
print("Daily run of ${mile} mile(s)");
}
weightTraining(int weights) {
print("Lifting ${weights} lbs");
}
}
Boxing
The Boxing mixin defines practicing punches behavior of an athlete. As per our requirements, only athletes are allowed to practice punches. In such cases, we may want to restrict the usage of mixin only by classes of type Athlete. We can apply such restriction on Boxing mixin by using on keyword followed by the Athlete - the class which is allowed the usage.
mixin Boxing on Athlete {
punch(int n) {
print("Boxer practicing ${n} punches");
}
}
Using Mixins
In this section, you'll see examples of using mixins defined earlier.
Artist class
The artist makes landscapes sketches. It defines sketchLandscape() to do so. This method calls sketch(...) method from Sketching mixin.
class Artist extends Person with Sketching {
sketchLandscape() {
sketch("Making landscapes sketches");
}
}
Engineer class
The engineer does make building sketches and reads research on building construction. The sketchBuildings() method uses sketch() method from Sketching mixin. The readResearchPaper() calls dailyReading(topic) from Reading mixin.
class Engineer extends Person with Sketching, Reading {
sketchBuildings() {
sketch("Sketching engineering drawings");
}
readResearchPaper() {
String topic = "Building Construction";
dailyReading(topic);
}
}
Doctor class
The doctor reads health reports and does workouts to keep it. The readReports() method uses Reading mixin. The workout() method uses Exercise mixin to carve personalized workout plan.
class Doctor extends Person with Reading, Exercise {
readReports() {
String topic = "covid";
dailyReading(topic);
}
workout() {
running(1);
weightTraining(10);
}
}
Athlete class
The athlete is a person as well like other people we discussed so far. All athletes do their exercise, and have a general workout routine. The method generalRoutine() provide the general workout routine definition.
class Athlete extends Person with Exercise {
generalRoutine() {
running(2);
weightTraining(20);
}
}
Boxer class
The boxer is a Athlete who does boxing. The Boxing mixin provides the punch() to define punchPractice() method for boxer. The routineExercise() method defines exercise routine for this specific athlete with help of Exercise mixin.
class Boxer extends Athlete with Boxing {
punchPractice() {
punch(100);
}
routineExercise() {
running(4);
weightTraining(40);
}
}
Running Code
In this section, let's run all the methods for each class.
void main() {
print("Artist");
Artist artist = Artist();
artist.sketchLandscape();
print("\nEngineer");
Engineer engineer = Engineer();
engineer.sketchBuildings();
engineer.readResearchPaper();
print("\nDoctor");
Doctor doctor = Doctor();
doctor.readReports();
doctor.workout();
print("\nBoxer");
Boxer boxer = Boxer();
boxer.punchPractice();
boxer.routineExercise();
}
Output:
Artist
Making landscapes sketches
Engineer
Sketching engineering drawings
Daily reading on Building Construction
Doctor
Daily reading on covid
Daily run of 1 mile(s)
Lifting 10 lbs
Boxer
Boxer practicing 100 punches
Daily run of 4 mile(s)
Lifting 40 lbs
Summary
In this article, we learned what Mixins are used for and how to use them to share common code across classes. We learned that inheritance is used when there's is a type of relationship. Mixins are used to share code for common behaviors across unrelated classes.
Check out the Dart Vocabulary Series for other Dart stuff.
Check out YouTube Video
Source Code
Please checkout the source code at Github here
References
Happy Darting :)
_Liked the article ? Couldn't find a topic of your interest ? Please leave a comment or reach out at twitter about the topics you would like me to share !
BTW I love cupcakes and coffee both :)_
Follow me at Medium